What is WBTC, and how does it differ from Native BTC

Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is an ERC-20 Ethereum token pegged 1:1 to Bitcoin (BTC). In other words, each WBTC represents one Bitcoin held in reserve. This “wrapping” process locks real BTC in custody and mints an equivalent token on Ethereum, making Bitcoin’s value usable in Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem.
Bitcoin itself runs on its blockchain, optimized for security and decentralization. By contrast, WBTC runs on the Ethereum network. Because Ethereum supports smart contracts, WBTC can interact with decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and other DeFi protocols. In essence, WBTC “unwraps” Bitcoin to the Ethereum world, letting BTC holders trade, lend, or stake their value without selling their Bitcoin.
How Wrapped Bitcoin Works
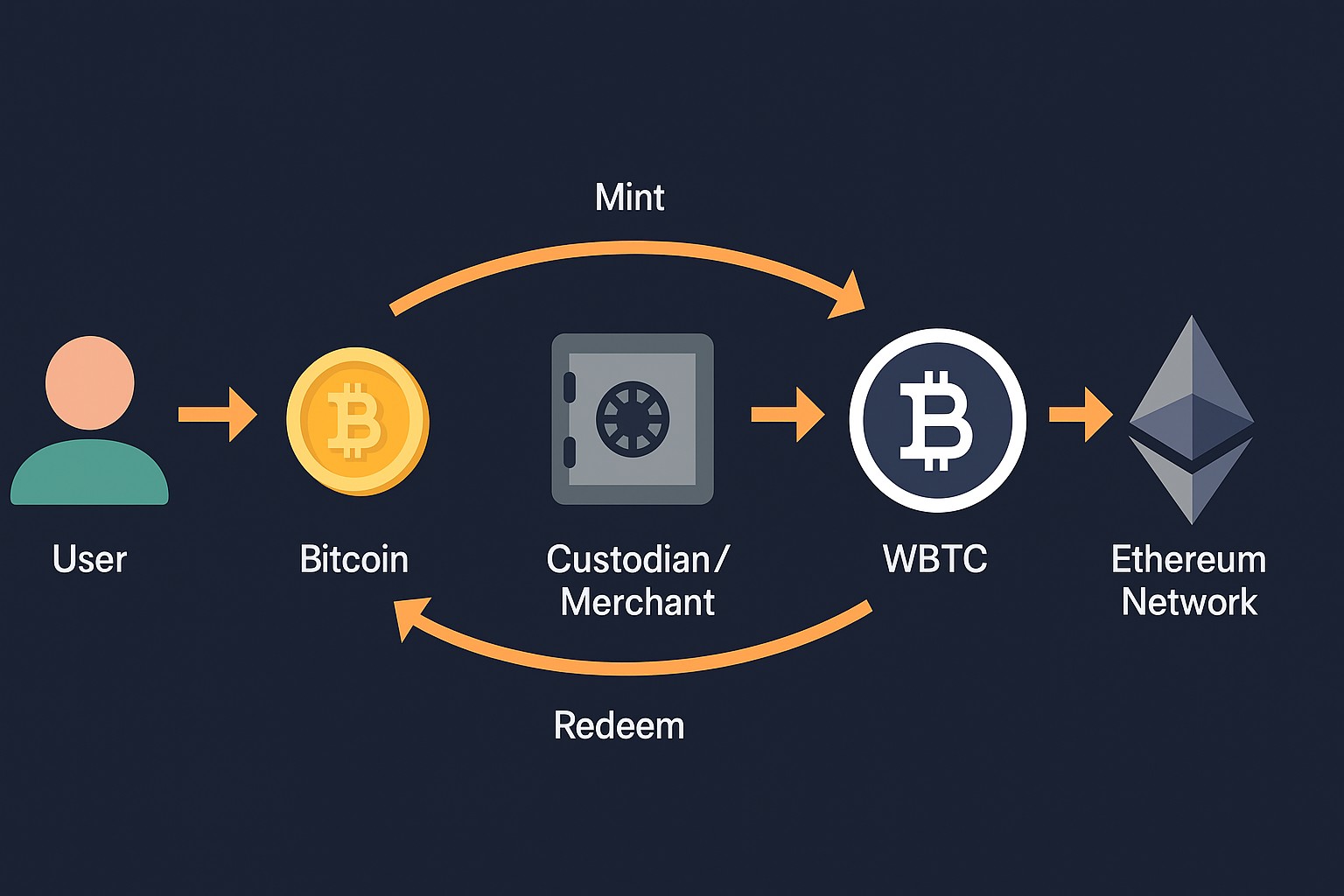
Wrapping Bitcoin involves a mint-and-burn process. When a user wants WBTC, Users who want to send 1 BTC to a custodian or merchant in the WBTC network. The custodian holds that BTC in reserve, then mints 1 WBTC token on Ethereum for the user. The user can then use that WBTC as an ERC-20 token. To redeem, the user burns (destroys) their WBTC, and the custodian releases 1 BTC back to them. This keeps WBTC always backed 1:1 by real Bitcoin.
- Custodial Mechanism: WBTC relies on approved custodians and merchants. Users must go through a merchant (often a regulated exchange or service like Kyber, Airswap, etc.) to mint or burn WBTC. These merchants perform KYC checks and coordinate with custodians (like BitGo) that lock up the BTC. Only these merchants can redeem WBTC for BTC.
- Ethereum Network: Once minted, WBTC functions like any other ERC-20 token. It inherits Ethereum’s speed (∼15-second blocks) and gas fees, and can be traded or used in smart contracts. This means transactions can be faster than Bitcoin’s ~10-minute blocks.
- Use in DeFi: Because WBTC is an ERC-20, it plugs seamlessly into Ethereum-based DeFi platforms. For example, one can supply WBTC to lending pools, trade it on decentralized exchanges, or stake it in yield farms.
WBTC vs BTC: Key Differences

WBTC and Bitcoin serve different purposes. The table below summarizes their main differences, followed by details on each aspect:
- Underlying Technology:
- BTC: Native to Bitcoin’s blockchain. Uses Bitcoin’s proof-of-work consensus. No smart contracts.
- WBTC: ERC-20 token on Ethereum. Uses Ethereum’s blockchain and smart contracts. Faster block confirmation, but it depends on Ethereum’s security model.
- Custody and Issuance:
- BTC: No custodian needed. Anyone can hold Bitcoin in their own wallet with private keys.
- WBTC: Issued by custodians (e.g., BitGo) and merchants. Users must trust these parties to hold the underlying BTC. WBTC minting and burning require going through those intermediaries.
- Security:
- BTC: Security is secured by Bitcoin’s blockchain (extremely high hash rate). No single point of trust.
- WBTC: Security partly relies on Ethereum’s network security, plus the custodial reserve. WBTC is as secure as the custodians and Ethereum contracts that back it. (Coinbureau notes WBTC is “highly liquid,” but custodians introduce trust/counterparty risks.)
- Use Cases:
- BTC: Best for store-of-value, peer-to-peer transfers, and as a decentralized digital gold. Ideal for long-term holding, payments on Bitcoin’s network, or any Bitcoin-native purpose.
- WBTC: Designed for DeFi. Perfect for using Bitcoin’s value in Ethereum applications – like decentralized lending, yield farming, trading on DEXs (e.g., Uniswap), or providing liquidity. It brings BTC liquidity to Ethereum finance.
By design, WBTC is not the same as “real” Bitcoin’s native form; it’s a representation. But it enables value from Bitcoin to interact with blockchains it otherwise couldn’t reach. Each WBTC token is redeemable for one BTC, ensuring transparency. In comparison, native BTC holders do not need to trust intermediaries to move or hold their coins.
The photo above shows Bitcoin (BTC) alongside other crypto tokens like Ethereum and Litecoin. WBTC brings Bitcoin into this multi-chain world as an ERC-20 token.
Use Cases of WBTC in DeFi

WBTC shines in the DeFi ecosystem because it unlocks Bitcoin liquidity for Ethereum protocols. Some common use cases include:
- Collateral for Loans: WBTC can be used as collateral on lending platforms (e.g., MakerDAO, Compound, Aave) to borrow other assets. This lets BTC holders leverage their crypto without selling.
- Yield Farming & Interest: By lending WBTC or providing it in liquidity pools, users earn interest or farm rewards. For instance, supplying WBTC to a money market pool might yield ~3% interest (as of late 2020). Many platforms also give governance tokens (like COMP from Compound) as extra incentives for lending or borrowing WBTC.
- Trading on DEXs: WBTC is widely traded on decentralized exchanges such as Uniswap and SushiSwap. This allows BTC value to flow into liquidity pools, increasing market depth and trading options. Traders can swap WBTC for ETH, stablecoins, or other ERC-20s without touching a centralized exchange.
- Cross-Chain Swaps: Some bridges and swap platforms (like TeleSwap) let you swap stablecoins or Ethereum tokens for WBTC, effectively buying Bitcoin without KYC. Likewise, WBTC can be unwrapped back into native BTC. This cross-chain flexibility is a major advantage.
- Collateral for Stablecoins: BTC collateral can back decentralized stablecoins (though most use ether or stablecoins, some DeFi apps allow BTC/WBTC as backing).
- DeFi Aggregator Participation: WBTC pools often appear in yield aggregators (Yearn, Harvest, etc.), combining BTC’s value with yield strategies automatically.
TeleSwap notes that wrapping BTC for DeFi “lets you enjoy attractive yields” on Ethereum while retaining the option to reclaim native BTC. In practice, millions in USD worth of WBTC are locked in Ethereum DeFi. (For example, WBTC supply is on the order of tens of thousands of coins, representing billions of USD.) This shows the demand for BTC exposure within DeFi.
Wrapping and Unwrapping: Converting Between BTC and WBTC
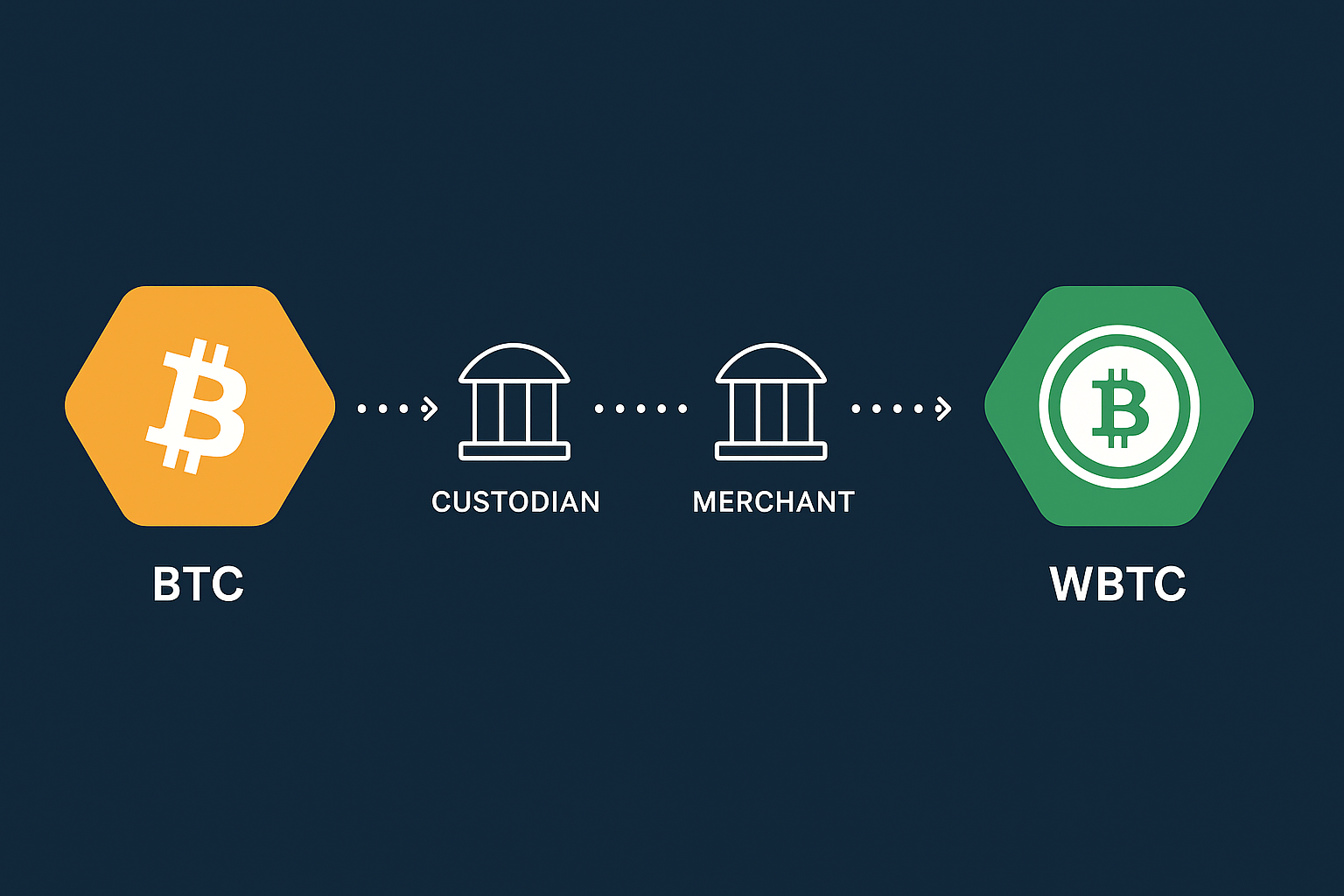
To get WBTC, Bitcoin holders typically mint it through a merchant. For example, a user sends BTC to a custodian via a merchant like Airswap or Kyber, and in exchange receives WBTC. Converting back is also possible: the user redeems WBTC for BTC (through a merchant/burn process). Note that while minting is often free, redeeming WBTC back to BTC usually involves a fee from the merchant.
Several platforms facilitate these conversions. Centralized exchanges (Coinbase, Kraken, Bitfinex) might list WBTC. Decentralized bridges (like the TeleSwap app) offer trustless swaps between BTC and WBTC or other cross-chain trades. TeleSwap, for instance, uses Bitcoin light-client bridges so users can swap tokens into BTC and back to tokens without KYC, with their BTC sent directly to their wallet.
Security Consideration: The wrapping process requires trust in the custodian/merchant. If those parties mismanage reserves, WBTC’s peg could break. Therefore, always use reputable services. TeleSwap’s approach, on the other hand, uses decentralized multi-signature Bitcoin addresses for trust-minimized swaps (see [Unlocking Trustless Bitcoin Bridges] for more).
Security and Custody: Trusting WBTC vs Bitcoin
- Bitcoin (BTC): Security comes from the Bitcoin network’s massive hash power. Bitcoin’s blockchain has never been compromised. You control your BTC with your private keys; no counterparty can seize it (unless you use a custodial wallet or exchange account).
- WBTC: Security is two-fold. On one side, WBTC lives on Ethereum, inheriting Ethereum’s protections. On the other hand, each WBTC is backed by BTC held in a vault by trusted custodian(s). If a custodian fails or is hacked, users could be at risk. Moreover, because merchants must manage keys for BTC custody, there’s an extra layer of trust. Coinbureau summarizes: “WBTC: Highly liquid and widely adopted, but centralized custodians introduce trust and counterparty risks.”
Therefore, WBTC is very useful and convenient, but it’s not as trustless as owning plain BTC. It’s best used when you need DeFi functionality. If your priority is maximum security or censorship resistance, holding BTC directly (in a secure wallet) is preferable.
Bridging WBTC with TeleSwap
For those looking to move Bitcoin into Ethereum DeFi (or vice versa) without centralized intermediaries, TeleSwap offers an intuitive solution. Through the TeleSwap app (app.teleswap.xyz), you can bridge tokens across chains in a trustless way. For example, swap ERC-20 stablecoins or tokens for native BTC directly into your Bitcoin wallet. Or, bridge your BTC to Ethereum as WBTC or other tokenized Bitcoin (like Runes). TeleSwap’s platform uses light-client bridges for security, so you always retain self-custody of your coins.
Ready to experiment? Use your Ethereum wallet (e.g., MetaMask, OKX Wallet) to connect to app.teleswap.xyz and swap into WBTC or Bitcoin in just a couple of minutes, with low fees. No KYC required.
Start swapping and bridging with TeleSwap
FAQ
What is Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)? WBTC is an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain that represents Bitcoin. Each WBTC is backed 1:1 by actual BTC held in reserve. It enables Bitcoin holders to use their BTC in Ethereum smart contracts and DeFi applications.
How does WBTC differ from BTC? WBTC is not native Bitcoin; it’s a tokenized version. The key differences are technological and custodial. BTC lives on the Bitcoin network (maximizing decentralization and security). WBTC lives on Ethereum and requires trusting a custodian to hold the backing BTC. In practice, use BTC if you want pure, long-term store-of-value or direct Bitcoin transactions; use WBTC if you need to interact with Ethereum DeFi using Bitcoin’s value.
Is WBTC safe? WBTC’s safety depends on the underlying custodians and Ethereum. The Ethereum network secures the token mechanics, but each WBTC relies on a custodian holding the actual BTC. Reputable custodians like BitGo are used, but there’s counterparty risk. Bitcoin itself remains more trustless. Always verify any WBTC service’s reserve audits or use decentralized bridges as much as possible.
What can I do with WBTC? WBTC opens up DeFi uses for Bitcoin. You can lend or borrow WBTC on platforms like Aave and Compound, swap it on DEXes like Uniswap, or provide liquidity in pools. This lets you earn interest, trade for other tokens, or mint stablecoins without selling BTC.
How do I convert WBTC back to BTC? To get back BTC, you “burn” WBTC through a WBTC merchant. In practice, you use an exchange or service that supports WBTC. They will swap your WBTC for BTC (you’ll receive actual Bitcoin to your wallet). Some platforms also allow direct “unwrap” functions. Note fees may apply on the way back. TeleSwap’s bridge can also convert WBTC to BTC in a trustless swap with Bitcoin light-client technology.
Where can I learn more or start swapping? See TeleSwap’s blog for tips on choosing Bitcoin wallets and bridging assets. For example, TeleSwap’s academy blog on top Bitcoin wallets recommends secure wallets like Xverse or Leather for receiving bridged BTC. When you’re ready, try the TeleSwap app at app.teleswap.xyz to swap between Ethereum tokens and native BTC in minutes.




